In-Kernel Intrusion Detection Systems using eBPF/XDP
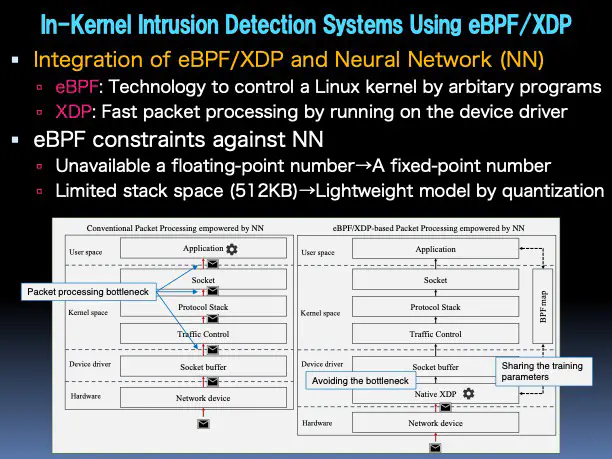
eBerkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) and eXpress Data Path (XDP) enable fast in-kernel packet processing without passing packets to the user space. Several studies pointed out the possibility of eBPF to realize intrusion detection systems (IDSs) empowered by simple machine learning (ML) algorithms, e.g., Decision Tree, in the kernel space. To ensure the kernel stability and safety, the eBPF constraints has strict constraints. e.g., violating the floating-point number, which makes it difficult to implement a neural network (NN), widely used in machine learning, in the kernel space. In this research, we aims at investigating the potential of eBPF/XDP-based packet processing empowered by the NN 12. More specifically, we first train the floating-point NN and quantize it to the fixed-point NN with 8-bit integer values in the user space. We then implement the lightweight NN in the eBPF/XDP program, which is running on the kernel space. We aim at realizing a lightweight and fast in-kernel intrusion detection system based on integer-only-inference using eBPF.
-
T. Hara and M. Sasabe, ‘‘On Practicality of Kernel Packet Processing Empowered by Lightweight Neural Network and Decision Tree,’’ to be presented at the International Conference on Network of the Future (NoF 2023), pp.1-9, Oct. 2023. (full paper). ↩︎
-
H. Taguchi, T. Hara, and S. Kasahara, “Unsupervised Real-Time In-Kernel Intrusion Detection System Using Autoencoders and eBPF,” IEICE Transactions on Communications, pp. 1-11, vol. E109-B, no. 2, Feb. 2026. doi: 10.23919/transcom.2025EBP3028 ↩︎